UEFI vs. BIOS – What’s the Differences and Which One Is Better
Read in বাংলা
UEFI and BIOS are two different types of motherboard firmware. Some users are confused about the two. In this post, I will illustrate you the main differences between UEFI and BIOS by giving you a UEFI vs BIOS, and show you how to convert MBR disk to GPT to support UEFI boot mode.
To know what is MBR and GPT click here 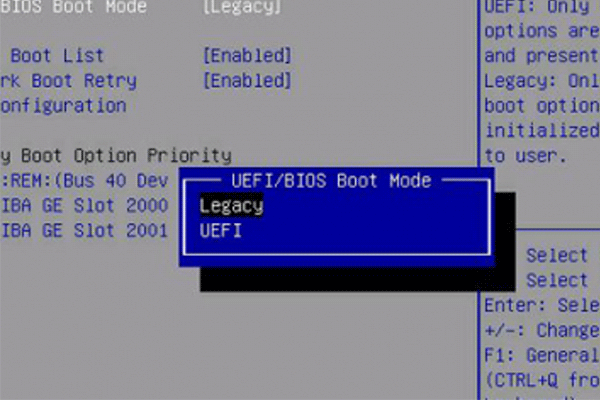
First you need to know what is UEFI and BIOS.
UEFI
UEFI is the abbreviation of Unified Extensible Firmware Interface, which is a firmware interface for computers and it works as a "middleman" to connect a computer's firmware to its operating system. It is used to initialize the hardware components and start the operating system stored on the hard disk drive when the computer starts up.
UEFI possesses many new features and advantages that cannot be achieved through the traditional BIOS and it is aimed to completely replace the BIOS in the future.
UEFI stores all the information about initialization and startup in a .efi file, a file stored on a special partition called EFI System Partition (ESP). The ESP partition will also contain the boot loader programs for the operating system installed on the computer.
It is because of this partition, UEFI can directly boot the operating system and save the BIOS self-test process, which is an important reason for UEFI faster booting.
Note: Some computer users use UEFI boot but still refer
to it as the “BIOS”, which may confuse some people. Even if your PC
uses the term “BIOS”, most modern PCs you buy today use UEFI firmware
instead of a BIOS. To distinguish UEFI and BIOS, some also call UEFI
firmware as UEFI BIOS, and BIOS is called Legacy BIOS or traditional
BIOS.
BIOS
BIOS is short for Basic Input/Output System, also known as system BIOS, ROM BIOS or PC BIOS. It is a firmware embedded on the chip on the computer's motherboard. BIOS firmware is pre-installed on the motherboard of a PC. It is a non-volatile firmware which means its settings won’t disappear or change even after power off.
It is not hard to understand how BIOS works. When your computer starts up, the BIOS loads and wakes up the computer's hardware components, making sure they are working properly. Then it loads the boot loader to initializes Windows or any other operating system you have installed.
What you need to know is, the BIOS must run in 16-bit processor mode, and only has 1 MB of space to execute in. In this case, it has trouble initializing multiple hardware devices at once, leading to a slower boot process when it initializes all the hardware interfaces and devices on a modern PC.
Although BIOS is a little bit outdated. There are still some users using BIOS, especially for users who have used their computer for many years. Sometimes they need to go to BIOS to change boot order if they have system boot issues.UEFI vs BIOS
Compared with BIOS, UEFI has the following advantages:
1. UEFI enables users to handle drives that are larger than 2 TB, while the old legacy BIOS couldn't handle large storage drives.
2. UEFI supports more than 4 primary partitions with a GUID Partition Table.
3. Computers who use UEFI firmware have faster booting process than the BIOS. Various optimizations and enhancement in the UEFI can help your system boot more quickly than it could before.
4. UEFI supports secure startup, which means that the validity of the operating system can be checked to ensure that no malware tampers with the startup process.
5. UEFI supports networking function in the UEFI firmware itself, which helps remote troubleshooting and UEFI configuration.
6. UEFI has a simpler graphical user interface and also has much richer setup menus than legacy BIOS.
After reading the above, you may find that UEFI has many advantages over BIOS. And it is due to these advantages, UEFI is regarded as a successor to BIOS.
However, UEFI is not supported by all computers or devices. To use UEFI firmware, the hardware on your disk must support UEFI. Besides, your system disk needs to be a GPT disk. If not, you can convert MBR disk to GPT disk with a professional partition magic. In this way, you can boot up your computer with UEFI mode successfully.
Tip: If your computer doesn't support UEFI firmware, you need to buy new hardware that supports and includes UEFI.
Convert MBR disk to GPT to Support UEFI Boot
Nowadays, UEFI gradually replaces the traditional BIOS on most modern PCs since many major hardware companies have switched over to UEFI use. If your computer supports UEFI firmware, you can convert MBR disk to GPT disk to use UEFI boot.
Well, how to convert system disk From MBR to GPT? Here I will show you a simple way to convert MBR to GPT without data loss with a professional partition manager.
MiniTool Partition Wizard is a professional partition manager trusted by millions of people. With its Pro Ultimate Edition, you can not only reconfigure hard disk with its basic features but also perform advanced features like recover lost partitions, convert system disk from MBR to GPT, change cluster size, convert dynamic disk to basic without data loss, convert NTFS to FAT and so on.
Step 1. Get the MiniTool Partition Wizard Pro Ultimate Edition by clicking the following button. Then use the Bootable Media Builder to create a bootable edition.
Step 2. Click the Bootable Media and follow the prompts to create a bootable USB drive or CD/DVD disc.
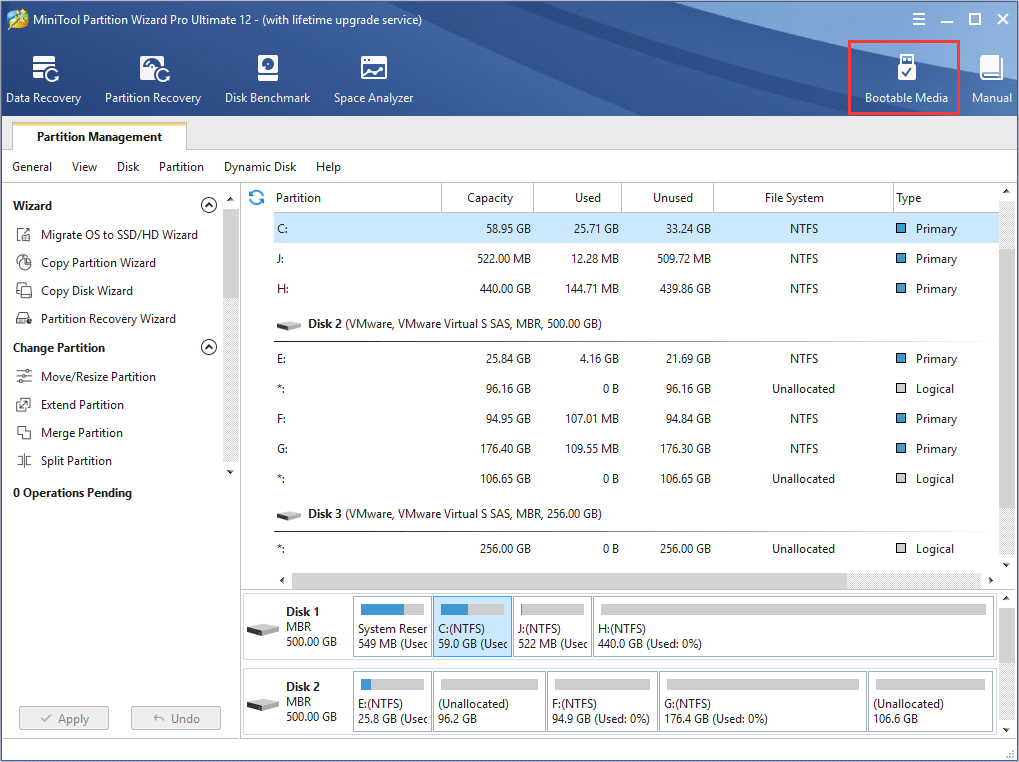
Step 3. Change the BIOS boot sequence to boot from the USB drive or CD/DVD disc to launch MiniTool Partition Wizard Bootable Edition.
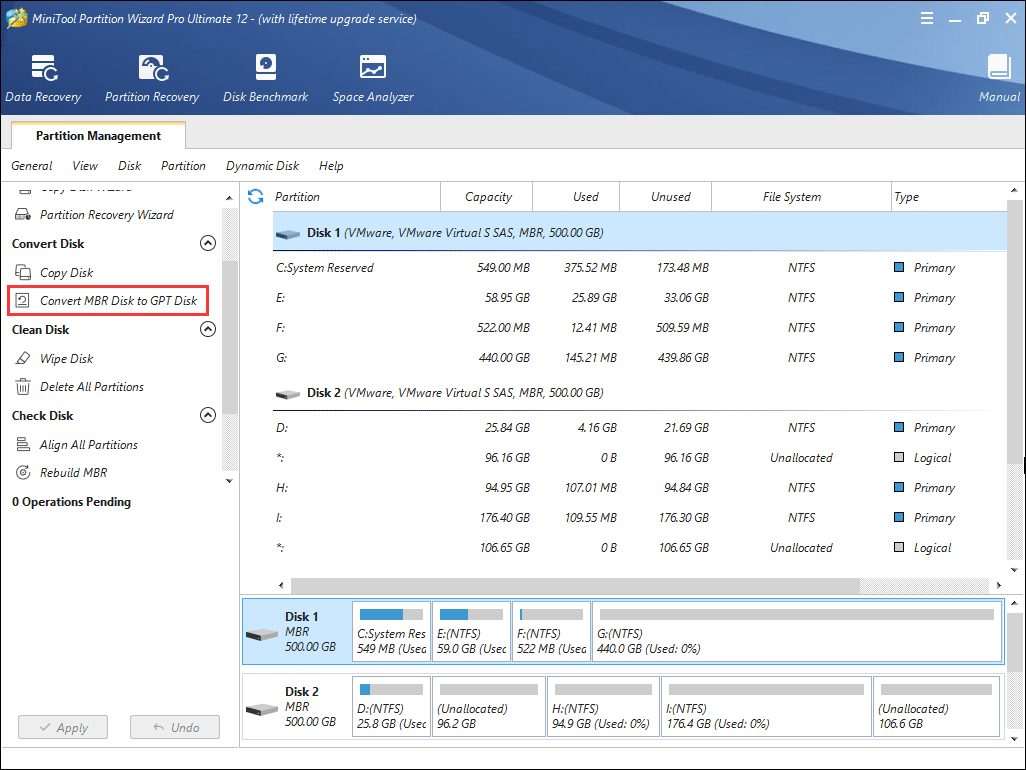
Step 4. In the bootable edition, choose system partition and select the system disk and choose Convert MBR Disk to GPT Disk from the left pane.
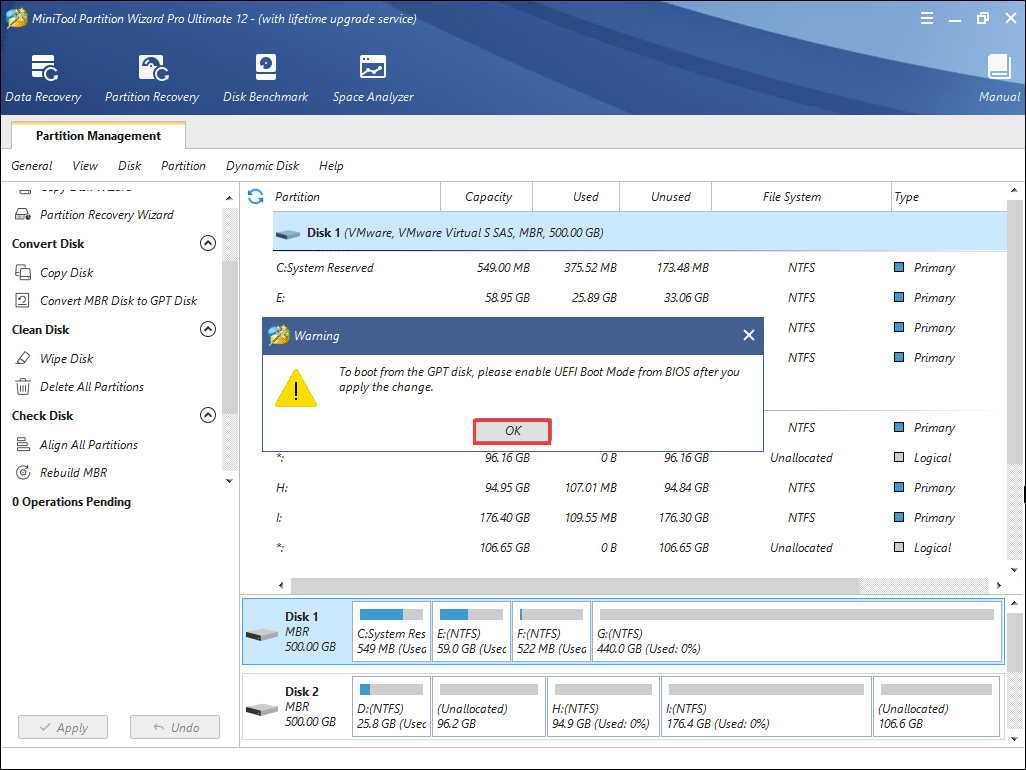
Step 5. Read the warning message and click OK.
Step 6. Click Yes to continue.
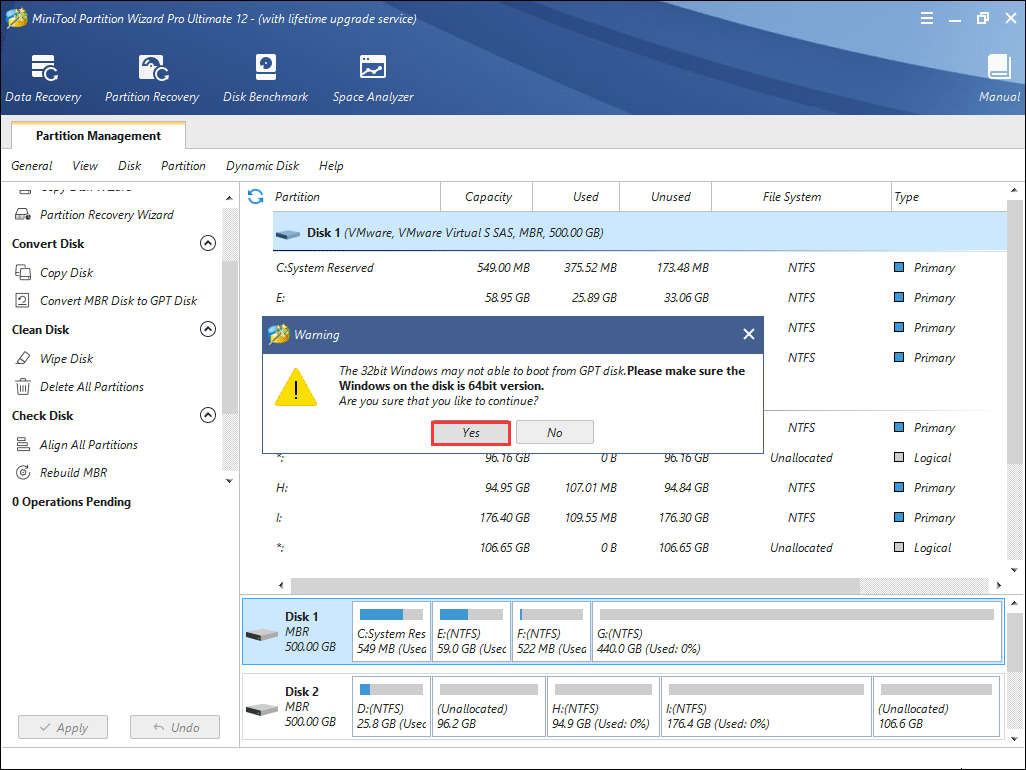
Step 7. You can see that the system disk has been converted to GPT disk, but this interface is the preview of conversion result. Click Apply on the upper left corner to allow the pending operations.
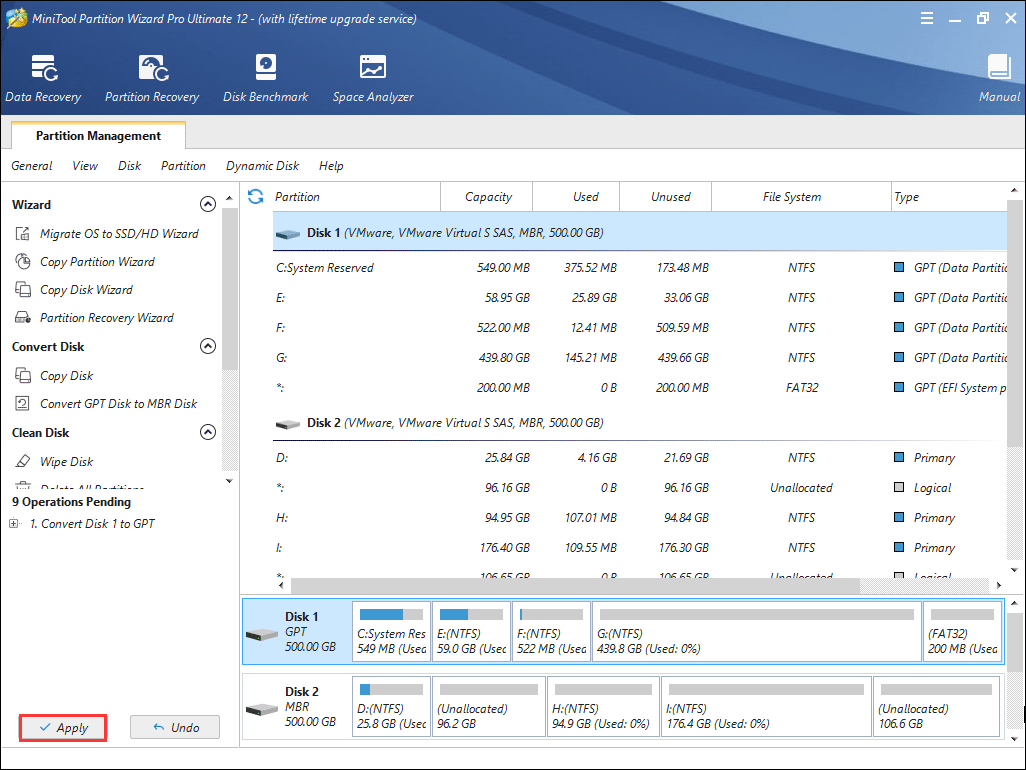
After conversion, you need to change BIOS boot mode to UEFI boot. Here you can follow the steps as below to access BIOS and switch to UEFI boot mode.
Step 1. Press the F2 or other function keys (F1, F3, F10, or F12), the ESC, or Delete key continuously when you boot your computer. For different computer manufacturers, the specific key to enter BIOS may be different. You can check your PC manufacturer support website for more specific details.
Step 2. From the BIOS Main menu screen, select Boot.
Step 3. At the Boot interface, select UEFI/BIOS Boot Mode, and press Enter.
Step 5. Then the UEFI/BIOS Boot Mode dialog box appears. Here you can use the up and down arrows to select UEFI Boot Mode, and then press Enter.
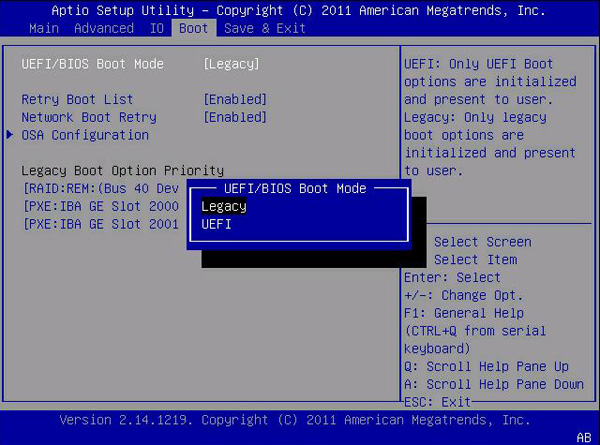
Step 6. Press F10 or a specific key depending on your BIOS to save the changes and exit the screen.
After that, your new computer will boot up and shut down faster than it would have with a BIOS, and you can use drives that are larger than 2 TB.
Note: Here no the MiniTool Partition Wizard Pro is not free. This wizard is shown because it's safe to convert MBR to GBT. By the way, you can try our free method.

No comments